27 February 2026
The Ultimate 2026 Guide to Amazon Video Ads Best Practices
TweetLinkedInShareEmailPrint 8 min read By Rick Wong Updated Feb 27, 2026 TL;DR What is the optimal len...

Google optimizes for research intent (learning), while Amazon optimizes for purchase intent (buying). Keywords on Amazon must target specific product attributes and high-intent phrases, not general informational queries.
On Google, no—paid and organic are separate. On Amazon, yes. Sales generated from Sponsored Products feed directly into your sales history and conversion data, which are primary factors for increasing your organic rank (the “Flywheel” effect).
Google rewards long-form, educational depth that builds trust. Amazon rewards skimmability and persuasion: use concise titles, benefit-led bullet points, and strong visuals to convert shoppers in seconds.
Google prioritizes authority and helpfulness (backlinks, E-E-A-T). Amazon prioritizes profitability (sales velocity, conversion rate, and price competitiveness).
Amazon SEO and Google SEO may look similar on the surface, but they are built for completely different goals. Google is designed to help people find information, while Amazon is designed to help people buy products. That difference changes how keywords work, how content is written, and how rankings are earned.
Google ranks pages that best answer a user’s question using signals like content quality, backlinks, and E-E-A-T, whereas Amazon ranks product listings that are most likely to convert into sales using signals like click-through rate, conversion rate, sales history, and price competitiveness. In practice, this means your keyword strategy, content format, and optimization tactics must be very different on each platform if you want consistent, scalable results.
Most sellers only realize this gap when their content ranks well on Google, but their Amazon listings stay buried. They recycle the same keywords and copy, expect similar results, and then wonder why impressions and sales do not move. In this guide, we will go beyond surface-level comparisons and walk through Amazon SEO vs Google SEO in a way that ties directly to strategy, execution, and performance.

The single biggest difference between the two platforms is search intent.
Industry benchmarks back this up. Average e-commerce websites convert about 2 to 4 percent of visitors, while Amazon often averages around 10 to 15 percent across categories, with some verticals going even higher. That means Amazon is optimizing every part of its ecosystem to answer one question: “Which product is this shopper most likely to buy right now?”
If you treat the two engines as identical, you run into predictable problems. On Google, you might write long, educational guides that build trust over several scrolls. On Amazon, that same wall of text will hurt skimmability, slow decisions, and reduce conversions. On the flip side, if you copy Amazon-style bullets to your site and write thin, salesy pages, Google’s quality systems are more likely to see that content as shallow and unhelpful.
Once you understand Amazon SEO vs Google SEO at the intent level, everything else starts to make sense: keywords, content length, formatting, and even how you measure success.

Amazon is not trying to be the “best search engine” in a general sense. It is trying to be the most profitable retail engine per search. That shapes how its algorithm behaves.
Most modern discussions still mention the Amazon A9 algorithm, but in practice, Amazon has evolved through A10 and multiple AI layers. The specifics change, yet the core commercial signals remain consistent:
When your metrics outperform competing listings for a search term, Amazon’s system learns that you are a more profitable choice and gives you more visibility. This self-reinforcing loop is often called the Amazon flywheel, because strong performance tends to generate even more visibility, clicks, and sales.
Keyword work on Amazon is less about answering questions and more about matching product attributes and use cases to purchase-ready shoppers. The job is to cover:
You do on-page work in the title, bullets, description, and A+ content, then fill the remaining gaps in the backend search fields. This holistic approach is what many sellers refer to as Amazon search term optimization, because you are tuning the entire listing around how real shoppers search, not just stuffing words into a single field.
A modern Amazon SEO strategy also has to consider AI-driven features. Amazon’s Rufus assistant reads product details, attributes, reviews, and Q&A to answer conversational questions and recommend products in line with shopper intent. If your attributes are incomplete or your content is unclear, Rufus has less to work with, which can quietly reduce your visibility as more shoppers use AI-led discovery.
On Amazon, “content quality” is measured in dollars, not just readability. That is why conversion rate benchmarks on the marketplace are significantly higher than those of regular e-commerce stores.
Your listing needs to:
This is where professional Amazon listing optimization services can make a big difference, because small improvements to CTR and conversion rate compound across organic rankings, Sponsored Ads efficiency, and total profit.
Tools also matter. Modern Amazon SEO tools and PPC platforms give you access to keyword data, share of voice, organic rank trends, and search term reports that would be impossible to track manually at scale.
Finally, it is almost impossible to talk about the key differences of Amazon SEO vs Google SEO without mentioning advertising. On Amazon, there is a much tighter feedback loop between paid and organic. Strong Sponsored Products campaigns create the initial traffic and sales signals the algorithm needs to trust your product.
That means organic ranking is rarely “free”. It is usually the result of smart alignment between Amazon SEO and PPC, where your ad targeting supports the same high intent keywords you want to rank for organically, and you monitor TACoS instead of focusing on ad spend in isolation.
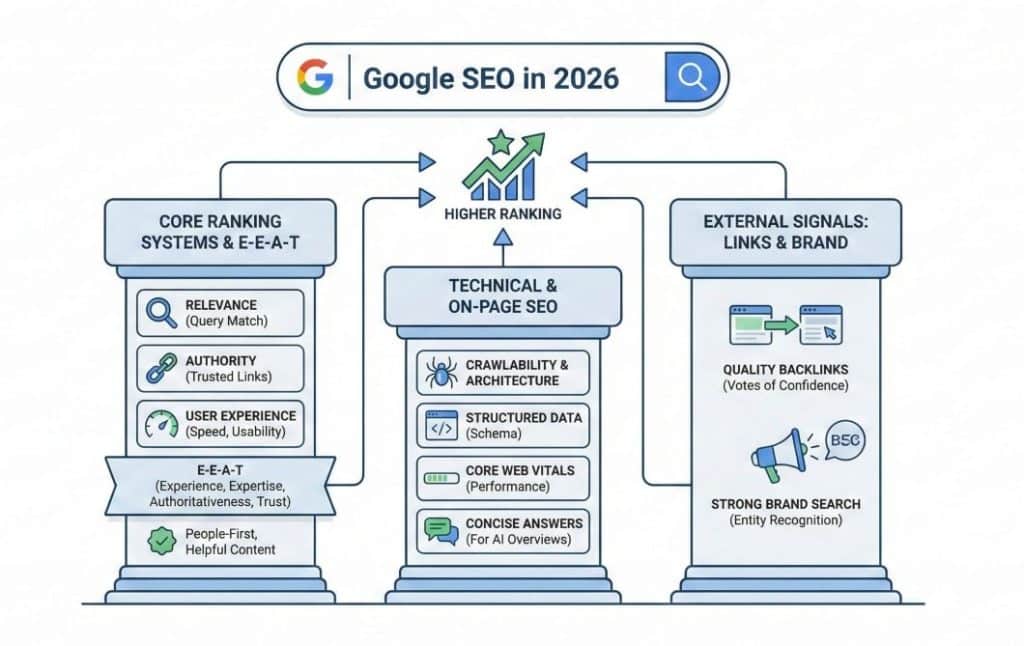
Google SEO job is broader. It has to answer everything from “how to unclog a sink” to “best CRM for law firms” and “buy blue running shoes size 10”. To do that at scale, its ranking systems focus on trust and helpfulness.
Google uses hundreds of signals, but three big buckets still matter most:
These are encapsulated in Google’s focus on high-quality, people-first content and E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness).
The Helpful Content and core updates in recent years aggressively downgraded articles that were thin, over-optimized, or clearly written for robots. Google now looks for:
If your site feels like a generic content farm, rankings are more volatile and harder to sustain.
On Google, technical SEO has a much larger footprint than on Amazon. You need to care about:
On page, best practice is still to:
Because Google now shows AI overviews and rich snippets for many queries, having a concise, direct answer near the top of your page is crucial for both traditional SEO and emerging GEO (Generative Engine Optimization).
Unlike Amazon, Google heavily relies on external signals. Quality backlinks from relevant, trusted sites act as votes of confidence. Strong branded search volume and entity recognition also help Google understand that you are a real business, not a fly-by-night site.
This creates a different growth pattern. With Google, you often invest heavily upfront in content and digital PR, then wait months for authority to build. With Amazon, you can accelerate much faster if you can afford initial ad spend and secure reviews.
To really understand the key differences of Amazon SEO vs Google SEO, keep this in mind. Google cares who you are in the broader web, while Amazon cares how your product behaves inside its marketplace.
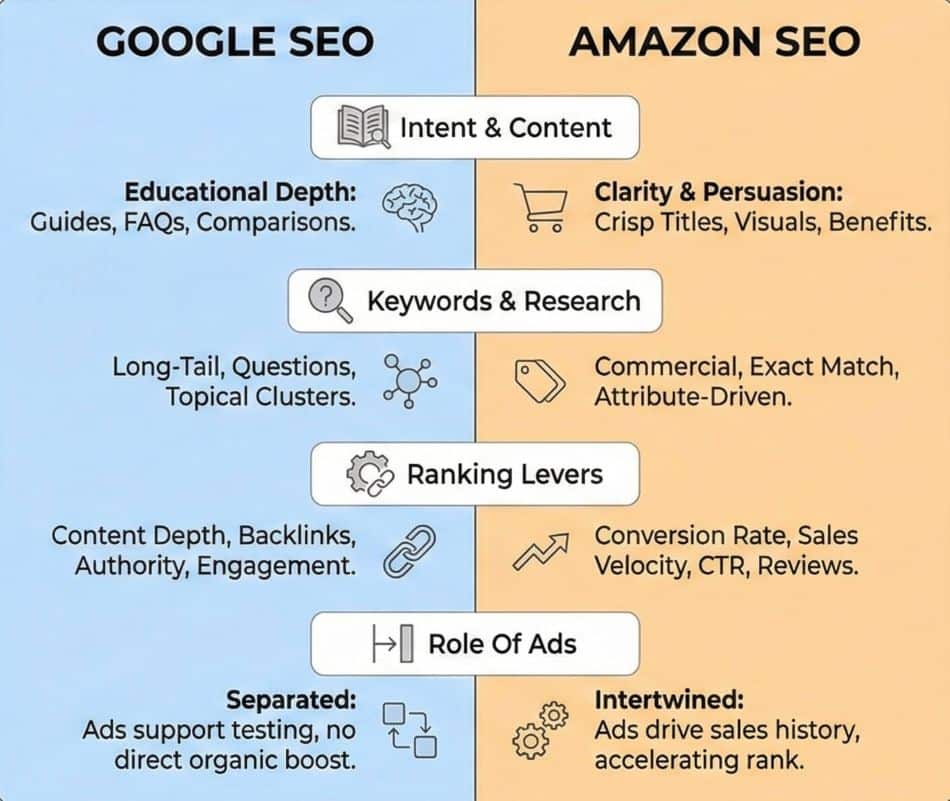
Let us put the theories side by side and look at what they mean for your daily work.
On Google, a 2,000-word buying guide can rank for dozens of long tail queries. On Amazon, trying to tell that whole story in your bullets will lower readability and likely reduce your conversion rate.
For Google, you might build an article around “best minimalist running shoes for flat feet”. For Amazon, you target “men’s stability running shoes” plus related attribute phrases, and you support that with backend terms and Sponsored Products.
Backlinks do not move your organic rank inside Amazon, but they can indirectly help by increasing traffic and sales. Similarly, sales and reviews do not directly improve your Google rankings, but they influence click-through rates on the SERP, which is still a valuable behavioral signal.
On Google, paid and organic are conceptually separated. Ads can support testing and visibility, but do not directly boost your organic ranking.
On Amazon, ads, organic rank, and profitability are deeply intertwined. Sponsored Products and Sponsored Brands campaigns create the traffic and sales history that feed the ranking system. This is where a thoughtful integration of Amazon SEO and PPC becomes a real competitive advantage.
Instead of treating ads and organic as different silos, winning brands use paid search to accelerate early visibility, validate keywords, and then double down on the phrases that drive both profitable ad sales and organic lift.
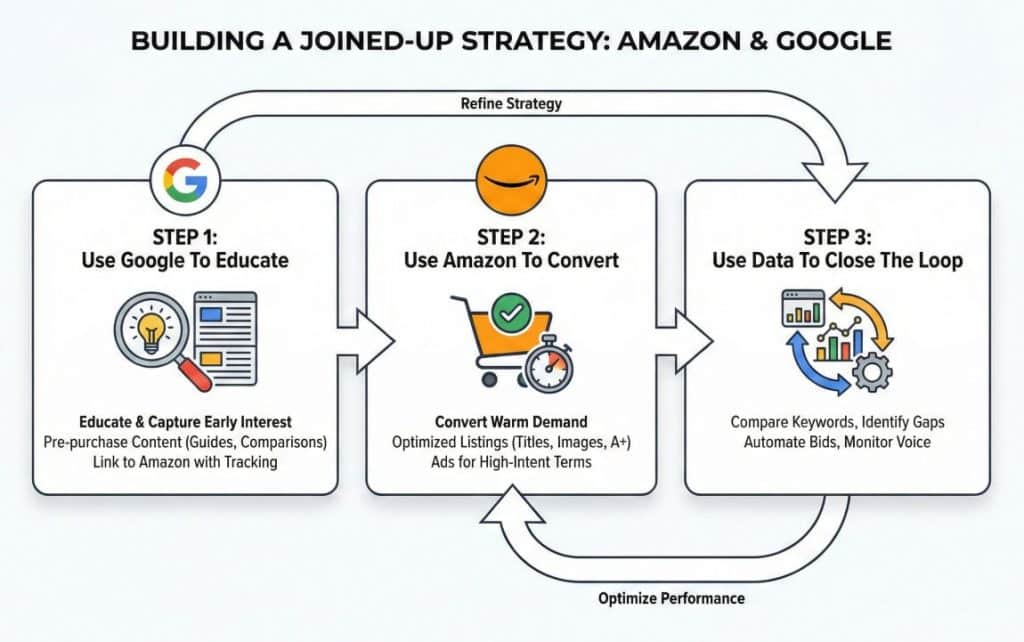
If you are serious about scaling your brand, you should not choose one search engine over the other. You should design a system where they reinforce each other.
On your own site, focus on topics that answer pre-purchase questions. Examples include:
These assets build trust, capture email subscribers, and show up in research phase searches. They are also ideal places to link to your Amazon listings with tracked URLs so you can attribute performance. This is a smart way to work on how to increase traffic to your Amazon listing without relying only on in-marketplace ads.
Once shoppers are ready to buy, your Amazon listing should be the fastest, lowest-friction way to complete the purchase. That means:
At this stage, you can lean on Sponsored Products, Sponsored Brands, and Sponsored Display to defend your branded keywords and target high-intent category terms. Over time, your increasing sales velocity and stronger metrics feed back into organic rank and support the Amazon flywheel effect.
Once both ecosystems are live, you can:
This kind of joined-up measurement is exactly where specialist partners are useful. A team that understands both marketplaces and ads can help you avoid working in silos.
At this point, the picture should be clear. Amazon and Google are not rival versions of the same thing. They are different stages of the same buyer journey.
If you treat them as identical, you will end up with content that underperforms in both places. If you embrace the key differences between Amazon and Google SEO and design your strategy around intent, signals, and user behavior, you can turn that difference into a real advantage.
Focus your Google presence on helpful, authoritative content that earns links and builds your brand. Focus your Amazon presence on high-converting listings, clean account health, strategic Amazon search term optimization, and a tight integration between Amazon SEO and PPC. Use each platform for what it does best, and let them feed traffic and trust into each other.
If you want a partner that lives in this intersection every day, talk to SellerMetrics about advanced Amazon PPC, listings, and GEO-informed content that works with both algorithms instead of fighting them. That is how you turn the key differences of Amazon SEO vs Google SEO from a confusing topic into a practical roadmap for growth.
You can start from the same core topics, but the phrasing and intent need to be adapted to each platform. Google rewards natural, question-based, and research-friendly keywords, while Amazon responds better to specific product terms and commercial attributes.
Yes, external traffic that converts can strengthen your organic visibility on Amazon because those sales still feed into your conversion and sales velocity metrics. You should track these clicks with Attribution links so you can see which campaigns genuinely move the needle.
Industry sources describe COSMO (Common Sense Model) as an AI layer that helps Amazon better match products to user intent by looking beyond simple keyword matches. It connects product attributes, behavior, and context so search results and AI answers feel more intuitive to shoppers.
Rufus is Amazon’s generative AI shopping assistant that reads your listing, reviews, and attributes to answer shopper questions and recommend products. To benefit from it, you need complete and accurate attributes, clear text that addresses common questions, and strong social proof.
Backlinks do not directly factor into Amazon’s internal ranking systems the way they do in Google’s algorithm. However, content and links that send qualified traffic to your listings can increase sales and indirectly improve organic rank.
Amazon benefits from built-in trust, saved payment details, and fast delivery expectations, so shoppers are primed to buy when they arrive. On your own site, visitors often have more friction, more doubts, and additional steps before checkout, which naturally depresses conversion rates.
On Amazon, you can often see ranking movement within days or weeks if you drive enough sales through PPC and a strong launch plan. On Googl,e it is normal for competitive terms to take several months or longer, because authority and links need time to build.
Sales performance relative to a specific keyword remains the strongest signal on Amazon, since each sale proves you are a good match for that query. Increasingly, contextual relevance informed by AI assistants like Rufus and systems like COSMO is closing the gap, so complete, high-quality listing data is more important than ever.
Yes, Amazon style guides expect the brand name first, followed by product type and key attributes. This helps with brand recognition, catalog consistency, and enforcement against copycats
Yes, repeating the same phrase unnaturally is more likely to hurt the shopper experience and confuse AI systems than to help rankings. It is far better to use natural language, cover related use cases, and rely on backend fields for variations instead of cramming everything into your visible copy.